There are links on this site that can be defined as affiliate links. This means that I may receive a small commission (at no cost to you) if you purchase something through the links provided on this website.
For details Click here.Global Axis and Local Axis in Blender: Understanding the Basics
Blender, a highly versatile 3D modeling software, offers users numerous tools and features to create stunning artwork and animations. Among these features, understanding the concepts of the global axis and local axis is essential for effective modeling and manipulating objects within the software. In this article, we will delve into the basics of global and local axes in Blender.
Global axis in Blender:-
In Blender, the global axis refers to the coordinate system that serves as a reference for positioning and orienting objects in the 3D environment. It consists of three axes: X (red), Y (green), and Z (blue), representing the horizontal, vertical, and depth directions, respectively. The global axis remains fixed and constant throughout the entire scene, providing a consistent frame of reference for all objects within it.
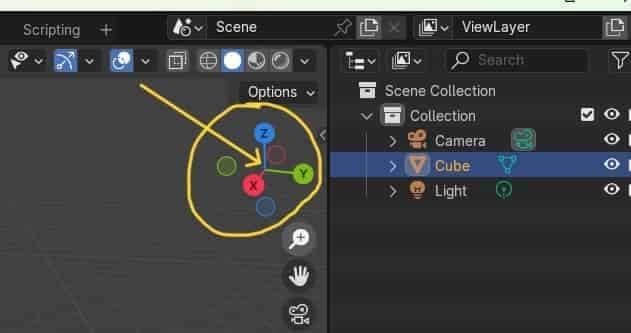
Local axis in Blender:-
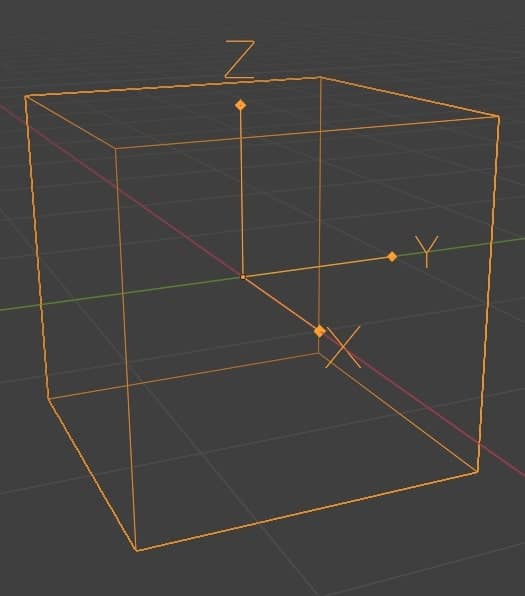
On the other hand, the local axis in Blender is specific to each object within the scene. It represents the object’s coordinate system and is aligned with its geometry or orientation. While the global axis remains fixed, the local axis can vary its orientation and position depending on how the object is transformed.
The local axis is crucial for precise modeling and manipulation of objects in Blender. When you select an object, Blender displays its local axis, helping you understand its current orientation. This ensures that any transformation, such as rotating, scaling, or moving the object, is relative to its local axis, allowing for precise manipulation.
To better understand the interaction between the global and local axis, consider the following scenario: You have a car model in your scene, and you want to rotate its wheels. By default, Blender uses the local axis of each wheel for rotation. Therefore, regardless of the car’s overall position or orientation in the scene, the wheels will rotate around their local axis.
However, you may also want to rotate the entire car as a single unit, maintaining its global position. In this case, you can switch to global axis mode, ensuring that the rotation affects the entire car by aligning it with the global axis.
summary:-
In summary, grasping the concepts of the global and local axes in Blender is essential for the effective modeling and manipulation of objects within the software. While the global axis provides a consistent frame of reference for all objects in the scene, the local axis enables precise transformations specific to each object. By understanding the interplay between these two axes, you can effectively create stunning 3D models and animations in Blender.
